Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon- Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari General de Catalunyaen/health-centers/hospital-universitari-general-catalunya
 Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
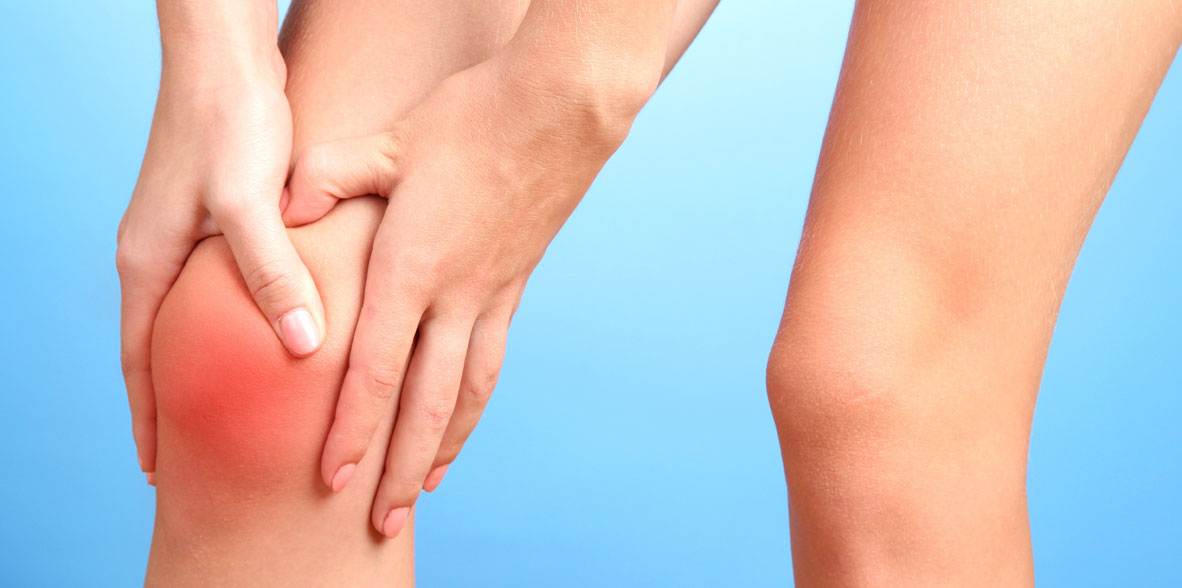
Knee pain is a common symptom that can be caused by a variety of medical conditions.
1. Soft Tissue Injuries:
- Symptoms: Pain, swelling, tenderness, difficulty moving the knee, bruising.
- Causes: Muscle strains, ligament tears (for example, the anterior cruciate ligament or ACL), tendonitis.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination, often using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for further evaluation.
- Treatment: Rest, physical therapy, immobilization with a splint, and, in some cases, surgery to repair serious injuries.
2. Osteoarthritis or inflammatory arthritis:
- Symptoms: Knee pain, stiffness, inflammation, loss of mobility.
- Causes: Osteoarthritis (cartilage wear), inflammatory arthritis (autoimmune disease), septic arthritis (infection).
- Diagnosis: Physical examination, blood tests, x-rays, ultrasound, MRI, joint puncture (in case of suspected infection).
- Treatment: Pain medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, surgery (in severe osteoarthritis cases).
3. Bursitis:
- Symptoms: Pain and tenderness in the front of the knee, swelling.
- Causes: Inflammation of the bursa (a pocket of fluid) in the knee due to injury or overuse.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination, x-rays, ultrasound or MRI.
- Treatment: Rest, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, bursa aspiration (in severe cases).
4. Meniscus Injuries:
- Symptoms: Pain, swelling, locking or "capping" of the knee, clicking sensation.
- Causes: Rupture of the meniscus (cartilage in the knee) due to twisting or trauma.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination, MRI.
- Treatment: Rest, physical therapy, surgery to repair or remove the damaged meniscus.
5. Chondromalacia Patella:
- Symptoms: Pain in the front of the knee, especially when going up or down stairs.
- Causes: Softening of the cartilage behind the kneecap.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination, x-rays, MRI.
- Treatment: Physical therapy, strengthening exercises, lifestyle changes.
6. Vascular or Nervous Injuries:
- Symptoms: Pain, abnormal sensations, weakness in the knee.
- Causes: Nerve compression, vascular disorders.
- Diagnosis: Imaging studies, nerve conduction tests.
- Treatment: Treatment depending on the underlying cause.
The precise diagnosis and treatment of knee pain depends on the underlying cause. A rheumatologist or orthopedic specialist will perform a detailed evaluation to determine the cause and recommend appropriate treatment. In some cases, imaging tests, such as x-rays or MRIs, may be used to obtain additional information. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent knee pain or if the pain is severe, as early diagnosis and proper treatment can help prevent long-term complications.