Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon- Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari General de Catalunyaen/health-centers/hospital-universitari-general-catalunya
 Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
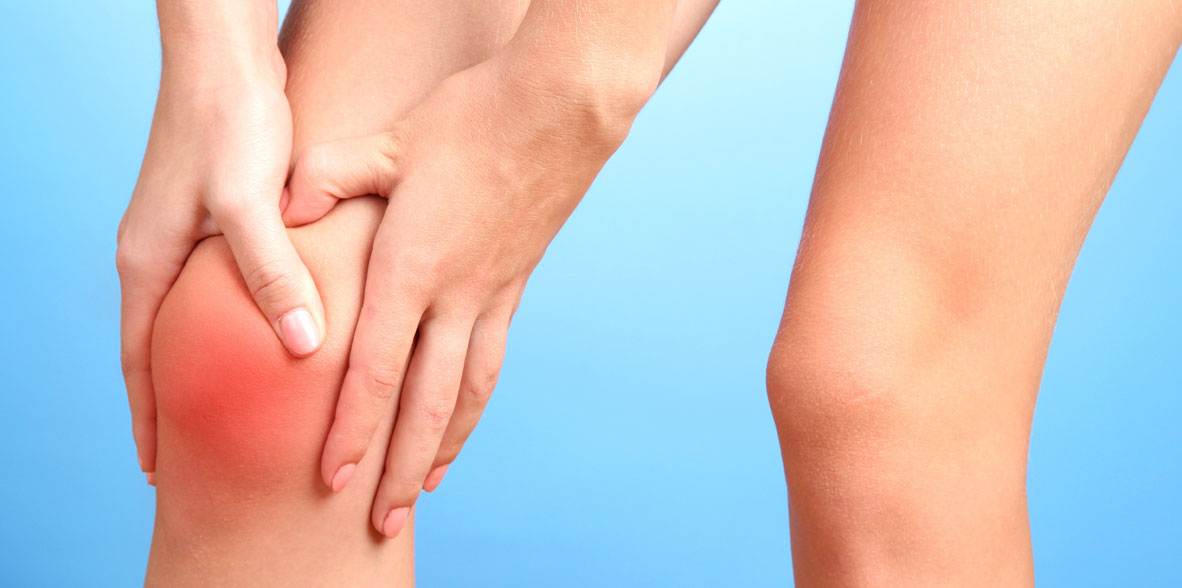
Rizarthrosis, also known as basal joint arthritis or thumb arthritis, is a condition that affects the joint at the base of the thumb. It can lead to pain and functional limitations.
Presentation Symptoms:
- Pain: Pain at the base of the thumb is the most common symptom. It can be a deep, aching pain and is often exacerbated by activities that require pinching or gripping.
- Swelling: Swelling at the base of the thumb may occur, which can lead to tenderness and a noticeable lump.
- Stiffness: Thumb joint stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of rest, is common. This can affect the range of motion and dexterity of the thumb.
- Weakness: Weakness in the thumb can result from pain and joint damage, affecting activities that involve fine motor skills.
- Crepitus: Some individuals may experience a grinding or grating sensation (crepitus) when moving the thumb joint.
Diagnosis:
Clinical Evaluation: A detailed medical history and physical examination by a healthcare provider, including an assessment of thumb function, pain, and range of motion.
Imaging Studies:
X-rays: X-rays of the thumb can reveal joint space narrowing, bone spurs, and other signs of arthritis.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound is used to evaluate the condition of soft tissues, including ligaments and tendons.
Treatment:
Conservative Management:
- Pain Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen can help manage pain.
- Splinting: A thumb splint or brace can provide support and reduce joint strain, particularly during activities that worsen symptoms.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding or modifying activities that exacerbate symptoms can help protect the thumb joint.
- Physical Therapy: Hand therapy with a certified hand therapist can provide exercises and techniques to improve thumb strength and function.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections into the joint may provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Orthopedic Interventions:
- Joint Protection: Procedures like joint fusion can stabilize the joint by removing the damaged surfaces and fusing the bones together. This eliminates pain but sacrifices joint motion.
- Joint Replacement: In advanced cases, joint replacement surgery may be considered. This involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial joint (prosthesis) to preserve joint motion while relieving pain.
Therapies and Home Remedies:
Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Thumb Exercises: Specific thumb exercises can help maintain strength and flexibility.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Modifying daily activities, using ergonomic tools, and adapting grip techniques can help reduce strain on the thumb joint.