
 Centro Médico Teknon
Centro Médico Teknon
What is carotid artery disease?
The arteries are responsible for transporting blood rich in oxygen from the heart to other parts of the body. The carotid arteries are the two main arteries thar transport blood from the heart, passing through the neck, to the brain.
Healthy carotid arteries are smooth and do not present any obstructions, which permit blood to flow freely to the brain, and to proportion oxygen, glucose and other nutrients that the brain cells need. With age, the carotid arteries generally accumulate plaque, a bloody substance composed primarily of oil and cholesterol. Plaque narrows the passage in the arteries and hardens them.
Carotid artery disease occurs when the carotid arteries become too narrow or obstructed, which limits the blood flow to the brain. Cerebral infarctions are produced when the obstruction of blood flow to the brain caused by the plaque although, more frequently, when small amounts of plaque come loose and flow to the brain (cerebral embolisms). So if carotid artery disease is not treated, it produces a cerebral infarction, since the lack of oxygen and other essential nutrients damages the brain. According to its gravity, a cerebral infarction may be fatal. In fact, cerebral infarctions are the third leading cause of death in the western world, and the principal cause of permanent invalids in older adults.
- Causes and Risk Factors

- Age
- Hypertension (high arterial pressure)
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise
- Family history of arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) or cerebral infarction
- Irregular heart rhythm, especially atrial fibrillation (condition diagnosed from the chambers when the chambers of the heart tremble and beat in an inefficient manner.
Diagram of the formation of an embolus, in side of the carotid artery (See image).
- Symptoms
In the initial stages it is possible not to have any symptoms of carotid artery disease and one of the first signs of the illness may be a cerebral infarction. Nevertheless, there may be some warning signs of a stroke which are called "mini-strokes" or "transitory ischemic attacks." The symptoms of the "mini-strokes" generally are temporary, they last from a few minutes to a few hours and should be treated as medical emergencies that require immediate treatment since they are critical indicators of future cerebral infarctions. Some of the symptoms of cerebral infarcts include:
-
- Weakness, numbness or tingling of one side of the body
- Inability to control movement on one side of the body
- Loss of vision or blurred vision in one or both eyes
- Inability to speak clearly
- Difficulty speaking or understand what other says
- Nausea or confusion
-
- Diagnosis
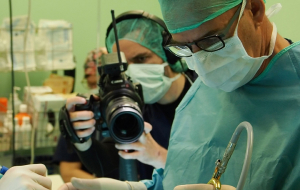
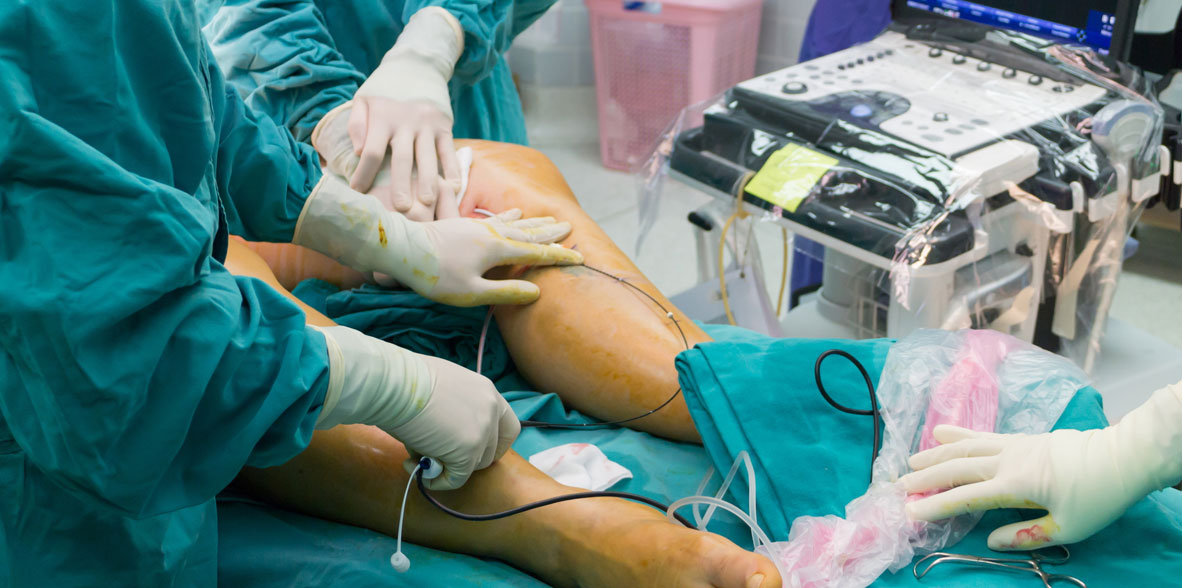
A non-invasive carotid Doppler can confirm the diagnosis of carotid artery disease and to determine its severity. If you experience symptoms of a mini-stroke (as previously described), consult a vascular surgeon who treats vascular diseases and can make available treatments, including the administration of medications, perform endovascular procedures with stent angioplasty and the surgical treatment referred to as a carotid endarterectomy.
All the diagnostic and therapeutic procedures should be performed by expert professionals who are experts in this type of illness.


Image 1 (left): Diagnosis by carotid Doppler of a bifurcation of the carotid arteries.
Image 2 (right): Film of stenosis of the carotid artery by angiography.
- Treatments
According to the severity of the illness, the options of treatment may include life style changes, medications or interventional procedures such as carotid endarterectomy, or stent angioplasty by means of endovascular techniques.
According to the international guides of clinical performance and the most recent medical literature, a carotid endarterectomy is recommended as first choice because it offers the best results both in asymptomatic patients (those who have not yet presented symptoms but with equal or stenosis greater than 70%) as well asymptomatic ones (who have presented symptoms of cerebral embolism).
The angioplasty with stent is a good alternative when patients who need intervention are high-risk surgical patients (severe cardiopathy, irradiated necks, intracranial lesions). Professionals who practice any of these techniques should have a great deal of experience and offer low rates of complications.

Carotid stent- parche of widening of the carotid artery after endarterectomy, specimen of carotid plaque extracted by endarterectomy
Only an expert vascular surgeon can offer you all these types of treatment and for you to likewise receive the most appropriate treatment for your disease. This is the case of our team.