
 Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon
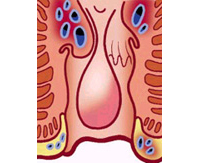
In the area of the rectum and anus there are a series of veins and arteries that form a set with the tissue that covers them. In situations of effort, irritation, etc., this set can become inflamed and cause discomfort, but returns to its normal state once the stimulus ceases. If the inflammation is intense and persistent, the discomfort increases and the disease we know as hemorrhoids occurs.
Hemorrhoids are a very common disorder. Between 50 and 75% of the population may be affected by them at some point in their lives.
- Why do they occur?
Hemorrhoids occur when blood presses too the walls of the veins of the rectum, causing them to dilate or even rupture. This increase in pressure can be due to several factors:
- Sitting too long, also on the toilet
- Stiffness and tension in the intestine
- Constipation or hard stools
- Diarrhea, which irritates the walls of the rectum
- Strong cough
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Lifting weights and making efforts in general
- Use of laxatives that produce dependence and loss of reflex function
- Exercise but avoid those that may irritate the area, such as horse riding or cycling for too long
- What are the symptoms?
 Internal hemorrhoids: They are usually distinguished by the presence of hemorrhages or prolapse, but do not cause pain. Patients complain of a feeling of rectal fullness, mucous exudate and dripping blood.
Internal hemorrhoids: They are usually distinguished by the presence of hemorrhages or prolapse, but do not cause pain. Patients complain of a feeling of rectal fullness, mucous exudate and dripping blood.- External hemorrhoids: Under the anal skin they increase in size over time by repeated dilation or thrombosis. The skin that covers them may distend until a skin appendage develops that prevents proper hygiene. Occasionally, in an external hemorrhoid, a clot will cause severe pain and bleeding if it erodes through the overlying skin. External hemorrhoids usually cause pain and itching even after minimal thrombosis because they are covered with skin with abundant innervation.
- How are they diagnosed?
- Medical history (anal pain and/or bleeding with or without relation to defecation, anal tumor, pruritus, bowel habit, etc.).
- Digital rectal examination. It must be carried out with caution, as it is usually very painful (in case of thrombosed hemorrhoid, fissure or abscess).
- Rectoscopia.
- Colonoscopy (preferably with sedation). In case of...
- Patients with a family history of colon neoplasia.
- Diagnostic doubts.
- Should I change my eating habits if I have hemorrhoids?
If you suffer from hemorrhoids, it is advisable to...
- Not eating very large, heavy, or high-fat meals
- Avoid spicy and spices in general
- No smoking
- Moderate, or better eliminate, the consumption of coffee and alcohol
- Salt retains fluid and, if taken in excess, is harmful
- Drink plenty of fluids or water: 6 to 8 glasses daily
- Foods rich in fiber (cereals, fruits, legumes, vegetables, etc.) are the most natural way to combat constipation (see food table).
- A diet rich in fiber is essential for the prevention and treatment of hemorrhoids.
- The optimal daily amount is between 25 and 30 g.
- Whole grains and flours contain more fiber than whites.
- Raw vegetables have more fiber than cooked ones.
- Fruit with skin has more fiber
Fiber content of some foods
BREAD AND CEREALS G/100 G Breakfast cereals* 4-30 Roasted corn 11 Pan integral 8,5 White bread 2,7 VEGETABLES Peas 7,9 White beans 7,3 Chickpeas 5,9 Lentils 3,9 VEGETABLES Broccoli 4,1 Carrot 3,7 Potato 3,5 Green bean 3,4 Cabbage 2,9 Cauliflower 2,1 Onion 2,1 Lettuce 1,5 FRESH FRUITS Pear 2,4 Peach 2,3 Orange 2 Plantain 1,8 Apple 1,4 Nuts Almonds 14 Peanuts 9,3 Nuts 7,7 - How to prevent hemorrhoids?
- Avoid being overweight
- Go to the bathroom when you feel the need without waiting for the last moment: then it may require more effort
- Not spending longer than necessary when using the toilet, it is not a library!
- Do not use rough or rough toilet paper: if necessary, start with moistened paper and then dry gently. It is also advisable to use the bidet or make warm water baths after deposition.
- Excessive hygiene is harmful, as it can dry out the skin too much.
- Stress and emotional tension produce stiffness and hinder bowel movements
- What is the treatment?
 Dietetic, hygienic, postural
Dietetic, hygienic, postural- Avoid obesity and constipation
- Avoid spicy foods, seasonings, spices and dressings, garlic, parsley, onion, mustard, tomato, vinegar, coffee, dark chocolate, tea and alcohol
- Avoid constant abdominal efforts; if the job requires sitting for many hours, getting up and walking for a few minutes every hour; Do not wear clothing that is too tight at the level of the abdomen, such as girdles or belts, especially in the case of pregnant women
- Exercise regularly, at least 30 minutes three times a week (walking, running or cycling on a stationary bike) in order to improve circulation
Ointments
- Corticosteroid anti-inflammatories: topical. They are inexpensive and very effective in inflammation at the beginning of thrombosis of both internal and external hemorrhoids. How to use: apply the ointment 2-3 times a day after defecation
- Contraindicated in pregnant women, bleeding hemorrhoids and for prolonged periods, and that produce local and systemic effects
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: also inexpensive, but slower-acting, hardly produce side effects. They are used as maintenance treatment
Oral Drugs
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Drugs to improve venous circulation
Surgical
Hemorroidectomía
Indicated as treatment of third and fourth degree hemorrhoids, large thrombosed prolapses, patients with coagulation disorders, patients treated with anticoagulants, even if they are carriers of internal hemorrhoids, and that with ligation there is a risk of aggravating the hemorrhage
It is carried out in the operating room. Availability of an anaesthetist
Various techniques are available: scalpel, scissors, laser, etc.
The incision is left closed, open or semi-openv It is important that during the intervention a sphincter control is maintained; The so-called mucous bridges (an area of unintervened mucosa) are left between the removed hemorrhoids, since, otherwise, there is a risk of anal stenosis. Good long-term results. The patient will be warned that they may experience recurrences, although they are less frequent than with the other techniques
Do regular checks with postoperative digital rectal examination.
Elastic bands
Indicated for second- and third-degree internal hemorrhoids at a distance of 1-2 cm from the pectine line. Ligation is carried out without the need for anesthesia. It hardly requires any equipment: a special vacuum cleaner equipped with rubber bands that strangle the hemorrhoid. Ligation is carried out in the consultation. The only requirement is to have the vacuum cleaner.
Other surgical techniques
- Hemorroidectomía circunferencial.
- Longo's technique
Other techniques
Indicated in hemorrhoids of first and second degree. They are simple techniques that are carried out in the consultation.
- Sclerosing injections. Irritating chemicals are injected.
- Photocoagulation. Pedicle fibrosis with diathermy.
- Cryocoagulation. Hemorrhoid coagulation by freezing with liquid nitrogen
Treatment in emergencies
Non-thrombosed inflamed hemorrhoids
- Sitz baths with warm water 2-3 times a day
- Local anti-inflammatory ointments (corticosteroids or other local anti-inflammatories)
- Diet rich in fiber and plenty of water
- Analgesics
- Drugs that improve venous circulation
Single thrombosed hemorrhoid
Surgical debridement (removal of the clot) under local anesthesia that is injected into the base of the hemorrhoid. The incision is left open. Warn the patient that he will bleed during grooming. (A common complication is a new thrombosis within a few hours.)Thrombosed and prolapsed (including ulcerated)
HemorrhoidsPatient evaluation. An urgent hemorrhoidectomy will often be required in the operating room.