Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon- Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari General de Catalunyaen/health-centers/hospital-universitari-general-catalunya
 Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
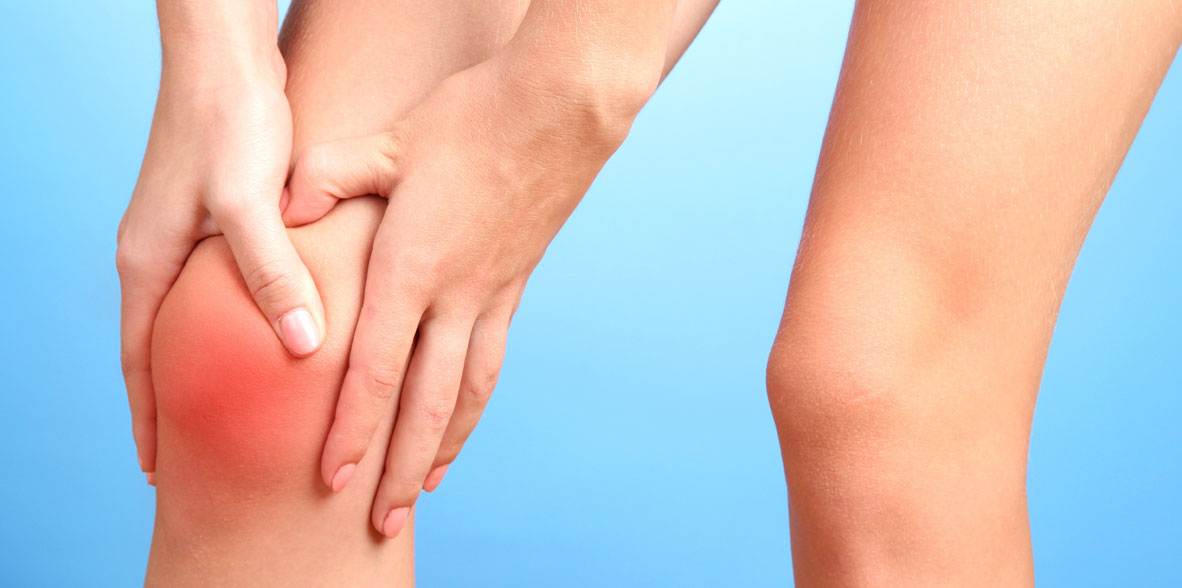
Curcumin is one of several substances present in turmeric or turmeric (Curcuma longa). It is responsible for the intense yellow color characteristic of this spice. Turmeric has been used for centuries in traditional medicine, particularly Ayurvedic medicine and Chinese medicine, due to its potential medicinal properties.
Clinical trials investigating the effectiveness of curcumin in osteoarthritis have yielded mixed results. Some studies have shown modest improvements in pain and function, while others have found no significant benefits compared to placebo.
A systematic review and meta-analysis published in 2016 concluded that curcumin supplementation may have a small to moderate effect on reducing osteoarthritis symptoms, including pain and stiffness, but more high-quality studies are needed to confirm these findings. .
Overall, although there is some evidence to suggest that curcumin may offer symptomatic relief in osteoarthritis, more research is needed to definitively establish its effectiveness.
Curcumin can be considered as an adjuvant therapy for people with osteoarthritis who are seeking alternative or complementary approaches to manage their symptoms.
It is important to note that individual responses to curcumin may vary and not all patients may experience significant benefits.
There is no standard dose of curcumin for osteoarthritis, as the optimal dosage may vary depending on factors such as supplement formulation, severity of symptoms, and individual patient characteristics.
Typical doses of curcumin supplements used in clinical trials for osteoarthritis range from 500 mg to 1,000 mg per day.
Curcumin supplements are often formulated with other ingredients such as black pepper extract (piperine) to improve absorption.
Curcumin is generally considered safe when taken at recommended doses, but it may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, and may not be suitable for people with certain medical conditions such as gallbladder disease.
Side effects of curcumin supplementation may include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, or indigestion.
As with any supplement, it is essential to discuss its use with your referring doctor, especially if you have other diseases or are taking any medication.