Morgenstern López Rudolf
- Els nostres serveis
Dr. Morgenstern was the first surgeon to develop and use in clinical routine a new, disruptive endoscopicsurgery for intervertebral body fusion. This surgery allows placing expandable cages with a skin incission of less than 15 mm. length, reduces a patient’s blood loss and is minimal invasive as no soft tissue and bone are removed during surgery. This endoscopic fusion surgery can be performed under local anesthesia, which is also unprecedent in spine surgery. This new, disruptive endoscopic fusion surgical technique intends to avoid big and invasive dissections to achieve lumbar interbody fusion as required in clssical spine surgery.
The disruptive procedure was developed by Dr. Morgenstern after decades of acquiring knowledge and experience with endoscopic surgery. His strong will to advance current surgical procedures to improve patients’ quality of life led him to develop and patent an endoscopic fusion technology that was first acquired in 2008 by the American company Interventional Spine Inc., based in California, U.S.A.
This sparked a fastchain of successful milestones. First, in 2011 the CE mark was obtained for the use of endoscopic fusion procedures in Europe. Dr. Morgenstern was the first surgeon worldwide to clinically use this procedure, by successfully implanting an expandable cage in a patient who was in strong pain due to a degenerated disk. More cases followed with an excellent outcome for endoscopic fusion surgery.In 2014 the technology was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its clinical use in the U.S.A.
Due to its reliability, accuracy and excellent outcome, the commercial introduction of this endoscopic fusion technology in the U.S.A. also was a great success. In consequence, Depuy-Synthes, a company of Johnson and Johnson, the biggest medical device company in the world, acquired this technology in January 2017.
Dr. Morgenstern has established himself as a clinical pioneer and a worldwide reference in minimally invasive, percutaneous and endoscopic spine surgery. He has produced numerous scientific international papers, patents and obtained an overwhelming amount of invitations to present his surgical technique in international conferences and teach in international workshops.
Examaple I Clinical Case




Indications for percutaneous endoscopic surgery
In cases of collapsed intervertebral disks and degenerative disc disease (DDD), now it is posible to restore the disk’s height with an expandable cage which is endoscopically introduced into the collapsed disk with a skin incission of less than 15 mm. of diameter. This surgical procedure can be performed under local anaesthesia. The patient resumes walking a few hours after surgerry and is usually discharged from the hospital approximately 24 hours after the surgery.
It is indicated for chronical lumbal pain and collapsed discs with sciatica. The pain usually is relieved in less than 24 hours after surgery.

Postoperative CT scan images showing an extremly collapsed L5/S1 disc (left) and the
same disk’s restored height after insertion and expansion of an expandable cage (right)
Pain relief is immediate or in less than 24 hours after the endoscopic fusion surgery. Walking is usually resumed 6 hours and hospital discharge in less than 24 hours after surgery.
Vídeo de la Cirugía
Explanatory video of an endoscopic fusion surgery
Example II Clinical Case



Example III Clinical Case endoscopic fusion of an 83-years old patient
This 83 years old lady with a degenerative instability had been unable to walk for the last 4 years. Inside her appartment, she would only walk a few steps with excruciating pain (VAS 9/10) using a cane, while going outside was only possible on a wheelchair.
She underwent a cement augmented percutaneous TLIF L4-S1 and an endoscopic decompression to alleviate her severe central canal stenosis at L4/L5. We placed both interbody cages through a single 12 mm skin incision, while the endoscopic decompression was done through an 8 mm skin incision.
You can see her smile at the end of this video while she is walking pain-free for the first time in many years just a few hours after surgery.
Concorde Lift Technology
Developed by Dr. Morgenstern



Images of an endoscopic fusion surgery
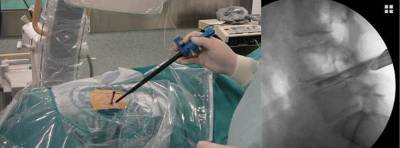
Endoscopic approach for the placement of an expandable cage through a skin incision of just 10-12 mm of length

A cage that can be expanded to up to 14 mm height restores the height of a degenerated, collapsed intervertebral disc

Fluoroscopic image of the placement and expansion of an expandable cage in a collapsed intervertebral disc. From left to right note the progressive expansion of the cage and the restoration of the intervertebral disc’s height

Post-operative radiologic control of the inserted expandable cage
| Morning | Afternoon | |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |
| Tuesday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |
| Wednesday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |
| Thursday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |
| Friday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |















