Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Quirónsalud Barcelonaen/health-centers/hospital-quironsalud-barcelona
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Quirónsalud Barcelonaen/health-centers/hospital-quironsalud-barcelona- Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Quirónsalud Barcelonaen/health-centers/hospital-quironsalud-barcelona
En el transcurso del tiempo, las recomendaciones para el tratamiento de la endometriosis han variado de forma importante. Desde los clásicos calmantes y anti-inflamatorios, pasando por la histerectomía radical con exéresis de ambos ovarios, hacia un tratamiento médico-quirúrgico más conservador, basado en la cirugía mínimamente invasiva por video-laparoscopia, intentando mantener los ovarios siempre que sea posible, puesto que es la fuente de feminidad por excelencia. Quitar los ovarios a una mujer joven es reducirla a un estado de menopausia.
Las distintas maneras de sufrir la endometriosis hace que las mujeres de modo individual y mediante consulta con su ginecólogo decidan la terapéutica más adecuada a su caso.
- Pharmaceutical treatment
- Contraceptives: such as the contraceptive pill or monthly injections, used in the treatment of mild forms of endometriosis and producing few side effects. However, they are not considered effective in more severe cases.
- Analogs (aGn-Rh): drugs that reduce the hormonal activity of the ovaries. They are administered over a period of six months, interrupting the production of oestrogen and bringing about a menopause. Endometrial tissue is frequently reduced in size, thereby alleviating pain caused by the disease.
- Surgical treatment
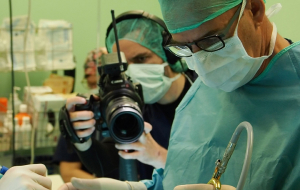
Conservative surgical treatment by means of laparoscopy is the most appropriate treatment for patients who wish to bear children, more radical treatment being reserved for hysterectomy and exeresis of both ovaries in patients who do not wish to have children or those with very severe endometriosis.
- Advantages
- Less time in hospital
- Less convalescence and faster recovery time
- Lower risk of post-operative adherencies
- Lower risk of infection
- Invisible scars
- Minimally invasive and conservative surgery
- Overall cost reduction
- Use of laser: precise application, depth control, greater destruction of infected cells, minimum blood loss, conservation of reproductive system
- ¿Qué aporta el láser a esta cirugía?
La aplicación del láser mediante laparoscopia es lo que se denomina "vídeo-laseroscopia". El más utilizado es el láser CO2 (dióxido de carbono), y entre sus ventajas destacan:
- Aplicación precisa
- Control de la profundidad del tejido lesionado
- Mayor destrucción de células afectadas y disminución del volumen tumoral. Gran interés en casos de endometriosis
- Mínimo sangrado intraoperatorio
- Reducción del tiempo quirúrgico
- Disminución de adherencias post-operatorias
- Conservación de la integridad del aparato reproductor de la paciente
- Anaesthetic
General anaesthetic is most commonly employed, given the frequent uncomfortable changes in posture required by this surgical operation, as well as abdominal distension as a result of the gas. Furthermore, thanks to advances in anaesthesia, there is a very low rate of complications.
- Risks
Video-laparoscopy ensures a much lower risk of surgical complication than conventional surgery. Multi-centre trials have shown an overall complication rate of 1/1000, the highest incidence being those involving accidents of a digestive nature and haemorrhage. However, these rates are also falling progressively.
- Could it be necessary to open the abdomen?
In the course of every endoscopic intervention, the real diagnostic image may differ from that envisaged clinically or by other complementary examinations, thus involving other organs that may make the technical resolution of this operation more difficult. In such cases, it would then be necessary for the benefit of the patient to open the abdomen. This is likely to occur in approximately 5 % of all laparoscopic interventions.